| Shigella | |
|---|---|
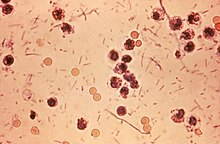 | |
| Photomicrograph of Shigella sp. in a stool specimen | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Bacteria |
| Phylum: | Proteobacteria |
| Class: | Gammaproteobacteria |
| Order: | Enterobacteriales |
| Family: | Enterobacteriaceae |
| Genus: | Shigella Castellani & Chalmers 1919 |
| Species | |
- This article is about the genus. For the disease, see shigellosis
Shigella is a genus of Gram-negative, nonspore forming, non-motile, rod-shaped bacteria closely related to Escherichia coli and Salmonella. The causative agent of human shigellosis, Shigella causes disease in primates, but not in other mammals. It is only naturally found in humans and apes. During infection, it typically causes dysentery. The genus is named after Kiyoshi Shiga, who first discovered it in 1898.
Phylogenetic studies indicate that Shigella is more appropriately treated as subgenus of Escherichia, and that certain strains generally considered E. coli – such as E. coli O157:H7 – are better placed in Shigella (see Escherichia coli#Diversity for details).
Shigella species are classified by four serogroups:[edit]Classification
- Serogroup A: S. dysenteriae (12 serotypes)
- Serogroup B: S. flexneri (6 serotypes)
- Serogroup C: S. boydii (18 serotypes)
- Serogroup D: S. sonnei (1 serotype)
Groups A–C are physiologically similar; S. sonnei (group D) can be differentiated on the basis of biochemical metabolism assays.[4] Three Shigella groups are the major disease-causing species: S. flexneri is the most frequently isolated species worldwide, and accounts for 60% of cases in the developing world; S. sonnei causes 77% of cases in the developed world, compared to only 15% of cases in the developing world; and S. dysenteriae is usually the cause of epidemics of dysentery, particularly in confined populations such as refugee camps.
[edit]Pathogenesis
Shigella infection is typically via ingestion (fecal–oral contamination); depending on age and condition of the host, less than 100 bacterial cells can be enough to cause an infection. Shigella causes dysentery that results in the destruction of the epithelial cells of the intestinal mucosa in the cecum and rectum. Some strains produce enterotoxin and shiga toxin, similar to the verotoxin of E. coli O157:H7and other verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. Both shiga toxin and verotoxin are associated with causing hemolytic uremic syndrome. As noted above, these supposed E. coli strains are at least in part actually more closely related to Shigella than to the "typical" E. coli.
Shigella invade the host through the M-cells in the gut epithelia of the large intestine, as they cannot enter directly through the epithelial cells. Using a Type III secretion system acting as a biological syringe, the bacterium injects IpaD protein into cells, triggering bacterial invasion and the subsequent lysis of vacuolar membranes using IpaB and IpaC proteins. It uses a mechanism for its motility by which its IcsA protein triggers actin polymerization in the host cell (via N-WASP recruitment of Arp2/3 complexes) in a "rocket" propulsion fashion for cell-to-cell spread. The most common symptoms are diarrhea, fever, nausea, vomiting, stomach cramps and flatulence. The stool may contain blood, mucus, or pus. In rare cases, young children may have seizures. Symptoms can take as long as a week to show up, but most often begin two to four days after ingestion. Symptoms usually last for several days, but can last for weeks. Shigella is implicated as one of the pathogenic causes ofreactive arthritis worldwide.
Each of the Shigella genomes includes a virulence plasmid that encodes conserved primary virulence determinants. The Shigella chromosomes share most of their genes with those of E. coli K12 strain MG1655.
[edit]Diagnosis
Shigella species are negative for motility and are not lactose fermenters. (However, S. sonnei can ferment lactose). They typically do not produce gas from carbohydrates (with the exception of certain strains of S. flexneri) and tend to be overall biochemically inert. Shigella should also be urea hydrolysis negative . When inoculated to a triple sugar iron (TSI) slant, they react as follows: K/A, gas -, H2S -. Indole reactions are mixed, positive and negative, with the exception of S. sonnei, which is always indole negative. Growth on Hektoen enteric agar will produce bluish-green colonies for Shigella and bluish-green colonies with black centers for Salmonella.
[edit]Treatment
Severe dysentery can be treated with ampicillin, TMP-SMX, or fluoroquinolones, such as ciprofloxacin, and of course rehydration. Medical treatment should only be used in severe cases. Antibiotics are usually avoided in mild cases because some Shigella are resistant to antibiotics, and their use may make the germ even more resistant. Antidiarrheal agents may worsen the sickness, and should be avoided. For Shigella-associated diarrhea, antibiotics shorten the length of infection.
+hb.jpg)

+hb.jpg)













 . Eggs become embryonated in water
. Eggs become embryonated in water  , eggs release miracidia
, eggs release miracidia  , which invade a suitable snail intermediate host
, which invade a suitable snail intermediate host  , including the genera Galba, Fossaria and Pseudosuccinea. In the snail the parasites undergo several developmental stages (sporocysts
, including the genera Galba, Fossaria and Pseudosuccinea. In the snail the parasites undergo several developmental stages (sporocysts  , rediae
, rediae  , and cercariae
, and cercariae  ). Thecercariae are released from the snail
). Thecercariae are released from the snail  and encyst as metacercariae on aquatic vegetation or other surfaces. Mammals acquire the infection by eating vegetation containing metacercariae. Humans can become infected by ingesting metacercariae-containing freshwater plants, especially watercress
and encyst as metacercariae on aquatic vegetation or other surfaces. Mammals acquire the infection by eating vegetation containing metacercariae. Humans can become infected by ingesting metacercariae-containing freshwater plants, especially watercress  . After ingestion, the metacercariae excyst in the duodenum
. After ingestion, the metacercariae excyst in the duodenum  and migrate through the intestinal wall, the peritoneal cavity, and the liver parenchyma into the biliary ducts, where they develop into adult flukes
and migrate through the intestinal wall, the peritoneal cavity, and the liver parenchyma into the biliary ducts, where they develop into adult flukes  .
.

